Getting Started
Install Marble
To install Marble, all you need to do is:
# npm
npm install --save marble-sdk
# yarn
yarn add marble-sdk
# pnpm
pnpm i marble-sdk
WAGMI user? Check out our connector: https://github.com/marblexyz/wagmi-connector.
Authenticate user
Once Marble has been added to your client-side code, you’ll need to log in users. We will generate a wallet for the user given their credentials. You can use the auth.loginWithEmailPassword function.
The following code snippet shows how to use the auth.loginWithEmailPassword function to authenticate a user and check that they are logged in.
import { Marble } from "marble-sdk";
const marble = new Marble();
// this will return false for a new user!
const isLoggedIn = await marble.auth.isLoggedIn();
/**
* loginWithEmailPassword
* Opens a modal that lets the user type their email and password to
* sign up, login, or send a link for forget password. Refer to the demo
* for how the base design looks like.
* Once the user successfully finishes login, fails in the process,
* or quits in the process, the function will return.
* @param {Object} configuration: Optiona object to pass in additional information.
* @param {string} configuration.email: If email is passed in, the input box for email will be pre-filled.
* @returns {loginState: "SUCCESS" | "FAILURE" | "ABANDONED"}
*/
const response = await marble.auth.loginWithEmailPassword();
// this will return true if the user logged in successfully!
const isLoggedIn = await marble.auth.isLoggedIn();
Once logged in, the user’s logged in session persists for half a day.
Marble and JSON-RPC providers
Marble SDK is compatible with existing Ethereum front-end APIs. As a result, marble-sdk bundles an Ethereum JSON-RPC provider that is compatible with most of the Ethereum and MetaMask JSON-RPC methods. This means that Marble SDK can be used wherever you are able to use existing wallets!
Connecting Marble to ethers
Here's an example of using Marble with ethers:
// Example with ethers
import { Marble } from "marble-sdk";
import { ethers } from "ethers";
const marble = new Marble();
// Create a provider
const provider = new ethers.providers.Web3Provider(marble.rpcProvider);
// Get a signer
const signer = provider.getSigner();
✉️ Are you using any libraries or frameworks we don’t support yet? Email us at team@marblewallet.com and tell us more! We’re happy to look into it for you and see how we can help.
Signatures
In order to sign messages or transactions, you can use the methods of your favorite provider. For example, with ethers you can use the signer you obtained earlier.
Similar to the login, when the user needs to sign a transaction, a modal will appear for the user on the application. The user can reject or confirm.
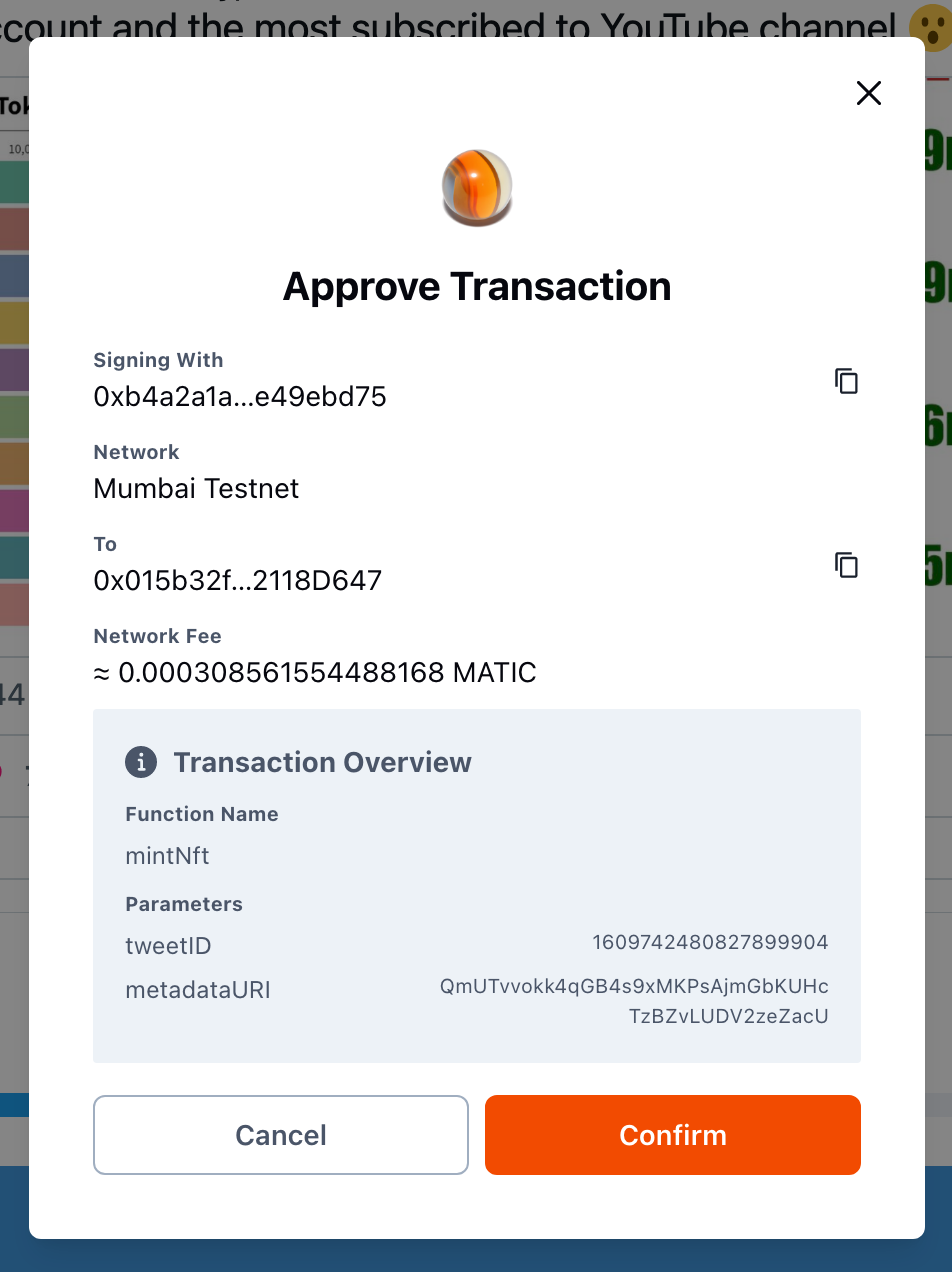
For any of signMessage, signTransaction, or send send operation, if the user clicks “Reject”, any of the sign functions will throw an error MarbleRPCError with the following information:
{
message: "User rejected signature request."
code: RPCErrorCode.UserRejectedRequest
}
Signing a transaction or message
// Sign a message or a transaction (after the user is logged in)
const signer = provider.getSigner();
const address = await signer.getAddress();
// Example: Signing Message
const result = await signer.signMessage("Hello world!");
// Example: Signing Transaction
const data = {
to: "0xbf9Db3564c22fd22FF30A8dB7f689D654Bf5F1fD", // Mumbai Faucet
from: address,
value: 100, // amt in wei
};
const result = await signer.signTransaction(data);
// Example: Ethereum RPC Call - eth_signTransaction
const signTransactionRequest = {
jsonrpc: "2.0",
id: 1,
method: "eth_signTransaction",
params: [
{
...data,
value: hexlify(data.value),
},
],
};
// You can also use the integrated provider to send RPC calls.
try {
const result = await provider.send(
signTransactionRequest.method,
signTransactionRequest.params
);
} catch (e) {
console.error(e.message); // on user rejection, should show "User rejected signature request."
console.error(e.code); // code would be RPCErrorCode.UserRejectedRequest which is importable through the SDK library.
}
Note: Currently, we don’t support the eth_sendTransaction method, since our API is connected to public providers. To use it, you will need to use your own provider and use the eth_sendRawTransaction method instead.